Pursuing a doctoral degree is a significant academic achievement that requires years of dedicated study, research, and intellectual rigour. Within the realm of doctoral studies, the terms ‘PhD candidate’ and ‘PhD student’ are commonly used, often interchangeably. However, a closer examination reveals that there are nuanced differences between these two designations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for both prospective doctoral students and those seeking to comprehend the various stages of the doctoral journey.
In this article, we delve into the disparity between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, shedding light on the roles, responsibilities, and progression associated with each stage. We explore the specific criteria that differentiate a student from a candidate and the various milestones marking the transition. Additionally, we delve into the responsibilities and expectations that accompany each designation, illuminating the unique experiences and commitments faced by PhD candidates and students.
Furthermore, we acknowledge the variability in terminology across international boundaries, academic institutions, and disciplinary fields, providing insights into how different contexts might influence the usage of these terms. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the contrasting aspects between a PhD candidate and a PhD student, facilitating informed conversations and a deeper appreciation for the intricate nature of doctoral education.
Introduction
Pursuing a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy) degree involves conducting original research in a specific field of study, making a significant contribution to knowledge, and demonstrating a high level of expertise. It is the highest academic qualification one can attain and is highly valued in academia, research institutions, and certain industries. A PhD signifies a deep understanding of a subject area, advanced analytical and critical thinking skills, and the ability to conduct independent research.
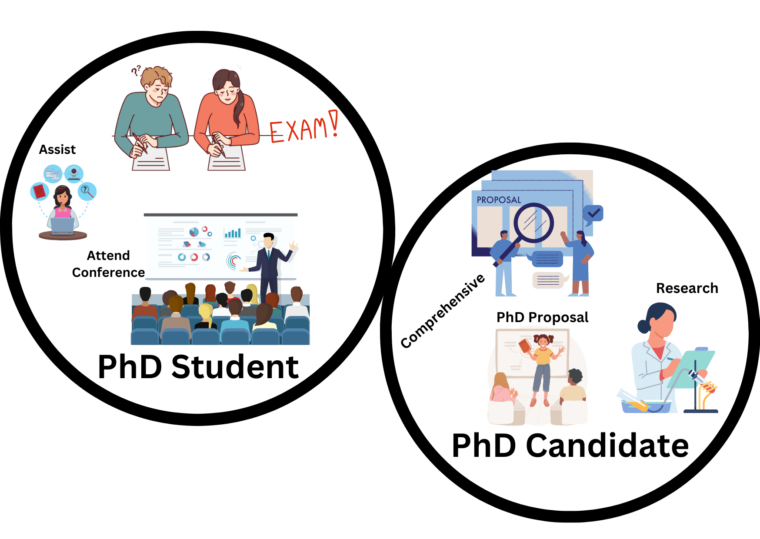
While the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two.
A PhD student typically refers to an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program, actively engaging in coursework and other program requirements. They are in the early stages of their doctoral journey and are working towards completing the necessary academic components of their degree.
On the other hand, a PhD candidate is typically someone who has progressed beyond the coursework stage and has advanced to the research phase of their program. They have usually completed comprehensive exams, passed a research proposal defense, and are actively engaged in independent research for their dissertation or thesis.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student. By exploring the criteria, milestones, and responsibilities associated with each designation, this article aims to clarify the unique experiences and progression of doctoral students. It also seeks to address the varying terminology used across different contexts and disciplines, enabling readers to grasp the intricacies of the doctoral journey and fostering informed discussions around this topic.
Through this article, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the journey from being a PhD student to becoming a PhD candidate and the distinct roles and responsibilities associated with each stage.
Who is a PhD Student?
A PhD student is an individual who has been admitted to a doctoral program and is actively engaged in pursuing their doctoral studies. They are at the initial stages of their doctoral journey, seeking to expand their knowledge, skills, and expertise in a specific field of study. PhD students play a vital role in academic research communities as they contribute to the generation of new knowledge and the advancement of their discipline.
PhD students are required to complete a set of coursework specific to their field of study. These courses are designed to provide a foundation in the discipline, enhance research skills, and broaden the student’s understanding of relevant theories and methodologies. Coursework may include seminars, advanced classes, and specialized topics. The specific coursework requirements can vary between programs and disciplines.
Example: Imagine a student named Alex who has just been accepted into a doctoral program in psychology. At this stage, Alex is considered a PhD student as they begin taking relevant coursework, attending seminars, and collaborating with faculty members. They are laying the foundation for their research and acquiring the necessary knowledge in their field.
Who is a PhD Candidate?
Advancement from being a PhD student to a PhD candidate typically involves meeting specific requirements set by the doctoral program. These requirements may vary depending on the institution and field of study but often include successful completion of coursework, exams, and other program-specific milestones.
One of the primary requirements for transitioning to a PhD candidate is the successful completion of coursework and exams. PhD students are expected to complete a designated set of courses, which provide a broad understanding of their field and research methodologies. They are also required to pass comprehensive exams, which assess their comprehensive knowledge and understanding of their research area.
As part of the transition to becoming a PhD candidate, students typically prepare and defend a research proposal. The research proposal outlines the scope, objectives, methodology, and significance of the intended research. The proposal defense may involve presenting the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who evaluate its feasibility, rigour, and contribution to the field. Additionally, PhD students often have to pass comprehensive exams, which test their knowledge of their research area and related disciplines.
If you are not familiar with writing PhD proposal and making PhD proposal presentation, then visit my articles on “How to Write PhD Proposal Presentation to the University” and ” How to Make a PhD Proposal Presentation to the University Panel”. These articles will guide you through the process of preparation and presentation of PhD proposal to the University panel.
When PhD Student attains status of PhD Candidate?
Upon successful completion of the requirements, PhD students are often granted candidacy status. Advancement to candidacy signifies that the student has demonstrated the necessary knowledge, skills, and potential to conduct independent research and contribute to their field. This status allows students to focus more exclusively on their research and dissertation work.
Once students become PhD candidates, there is a shift towards an increased emphasis on independent research. They are expected to dedicate a significant portion of their time and effort to conducting original research, collecting data, analyzing results, and making novel contributions to their field. The focus is primarily on their dissertation or thesis work, which serves as the culmination of their doctoral studies.
Example: Let’s consider a PhD student named Alex in the field of computer science. After completing their coursework and passing comprehensive exams, Alex develops a research proposal outlining their intention to investigate the applications of machine learning in cybersecurity. They present the proposal to a committee of faculty members, who assess the feasibility and potential impact of the research.
Alex successfully defends their research proposal and is granted candidacy status, transitioning from a PhD student to a PhD candidate. With candidacy status, Alex’s focus shifts towards conducting independent research. They spend considerable time collecting and analyzing cybersecurity datasets, developing and refining machine learning algorithms, and testing their effectiveness in detecting and preventing cyber threats.
As a PhD candidate, Alex works closely with their advisor, regularly discussing research progress, seeking guidance, and receiving feedback. They collaborate with other researchers in the field, attend conferences to present their findings and contribute to the scholarly community through publications. The focus is now on producing an original and significant contribution to the field of computer science through their dissertation.
The transition to PhD candidacy marks a critical stage in the doctoral journey, as it signifies the ability to independently drive research and make scholarly contributions. PhD candidates like Alex are immersed in the world of research, expanding knowledge, and pushing the boundaries of their field.
Variation in Terminology
Terminology related to PhD candidates and PhD students can vary internationally and among different academic institutions. In some countries, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” may be used interchangeably, while in others, there may be specific distinctions. For example, in the United States, “PhD student” is commonly used, while in the United Kingdom, “PhD candidate” is more frequently employed. Additionally, different universities or institutions may have their own terminology preferences, which can create further variation.
Terminology can also vary based on the disciplinary field of study. Different academic disciplines have their own conventions and terminology for referring to individuals pursuing a doctoral degree. For instance, in the sciences, one might encounter terms like “graduate researcher” or “doctoral candidate.” In the humanities and social sciences, the terms “PhD candidate” and “PhD student” are often used. This variation reflects the specific linguistic and cultural norms within different academic domains.
In Canada, for instance, doctoral students are commonly referred to as “PhD candidates,” regardless of their stage in the program. In Australia, “PhD candidate” is the preferred term for those who have completed the required coursework and have advanced to the research phase. In contrast, in the United States, “PhD student” is frequently used to refer to individuals at all stages of their doctoral studies.
Disciplinary variations can also be observed. In engineering, individuals pursuing a doctoral degree are often referred to as “PhD students” or “doctoral students.” In contrast, in the field of education, the term “PhD candidate” is commonly used to denote those who have advanced to the research and dissertation stage.
It is important to note that these examples represent general trends, and there can still be variation within specific institutions and programs. The usage of terminology can evolve over time and may be influenced by regional or institutional preferences.
Conclusion
The distinction between a PhD candidate and a PhD student holds significant importance in the realm of doctoral education.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different stages and responsibilities within the doctoral journey. A PhD student is in the initial stages of their program, actively engaging in coursework, research, and academic requirements.
On the other hand, a PhD candidate has advanced beyond coursework, passed comprehensive exams, and is focused primarily on independent research and the completion of their dissertation.