Personal Story: The Ripple Effect of Citations
I want to share a personal story that highlights the transformative power of citations in research. It all began when my research scholars and I delved into the realm of pomegranate pathology using image processing, a topic that held immense importance in the agricultural landscape.
Our journey led us to collaborate on groundbreaking research, with our findings addressing key issues in pomegranate cultivation. But what truly astounded us was the reception our work received from the academic community.
As citations for our research paper began to accumulate, we witnessed a remarkable ripple effect. Not only did our work attract attention from the computer science community, but it also resonated deeply within the broader agricultural sphere.
The influx of citations opened doors to a multitude of opportunities. We found ourselves inundated with invitations to workshops, offers to serve as reviewers and editors for renowned journals, and opportunities to participate in prestigious conference technical program committees.
The impact of citations extended far beyond mere recognition; it served as a catalyst for further engagement and collaboration. Researchers from diverse backgrounds reached out to us, eager to build upon our findings and contribute to the collective body of knowledge.
This experience was a testament to the significance of citations in research. It reaffirmed our belief in the value of producing high-quality, impactful work that resonates with fellow scholars and inspires future research endeavors.
So, to all the researchers striving to attract citations for their work, remember that each citation is more than just a number—it’s a testament to the relevance and significance of your research. Embrace the journey, and let the ripple effect of citations propel you towards greater heights of academic success.
Introduction
In the vast landscape of academia, where groundbreaking ideas and pioneering research emerge every day, it becomes crucial for researchers to not only produce exceptional work but also ensure that their contributions resonate and reach the wider scholarly community.
One significant measure of research impact is the citation count, which reflects the recognition and influences a paper garners over time. However, achieving a substantial citation count is not a matter of chance or manipulation; it requires a strategic and ethical approach.
In this article, we delve into the realm of legitimate practices that can amplify the visibility, citation counts, and recognition of your research paper.
Discover how you can navigate the scholarly landscape, captivate readers, establish credibility, and foster collaborations, all while staying true to the principles of integrity and excellence. Join us as we unlock the secrets to increasing citation counts in a legitimate way and ascending to new heights of recognition in the research community.
What is a Citation?
Citations are a technique to acknowledge the sources of the information that you used in your work. It also provides a crucial road map for your research approach, giving your readers the knowledge they need to locate that source again. You must cite any sources you utilise in your study, including books, journals, and the internet, in order to properly acknowledge the original author.
Why do Researchers Cite?
Researchers use citations not only to give credit to original creators and thinkers but also to add strength and authority to their own work. By citing their sources, scholars are placing their work in a specific context to show where they “fit” within the larger context of the research domain. Citations are also a great way to leave a trail intended to help others who may want to explore the conversation or use the sources in their own work.
Basically, citations give credit; bring strength and authority to your work; set your work in a certain context; and create a trail for future academics.
A. Importance of citation counts in research:
- Citation counts serve as a quantitative measure of the impact and influence of a research paper within the scholarly community. It indicates how widely the work has been acknowledged and referenced by other researchers.
- High citation counts signify that the research has made significant contributions to the field and has influenced subsequent studies, establishing the author’s credibility and expertise.
- For institutions and researchers, citation counts play a vital role in evaluating the quality and impact of research output, influencing funding decisions, career advancements, and academic rankings.
Example: Research papers with high citation counts often receive greater attention from funding agencies, leading to increased opportunities for grants and collaborations. Additionally, researchers with a strong citation record are more likely to secure prestigious academic positions or be invited to speak at conferences.
B. Benefits of increasing citation counts and gaining recognition:
- Increased visibility and reach: A higher citation count increases the visibility of your research, making it more discoverable by researchers working in the same or related fields. This can lead to wider dissemination and potential collaborations.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility: A research paper with a substantial number of citations enhances the author’s reputation within the research community. It demonstrates expertise, influence, and the ability to contribute valuable insights to the field.
- Career advancement opportunities: Researchers with a strong citation record often enjoy enhanced career prospects, such as securing tenure, obtaining prestigious awards, or being considered for leadership positions in academia or industry.
Example: A researcher who consistently achieves high citation counts may be invited to serve on editorial boards of reputable journals, review grant proposals, or participate in influential research initiatives. These opportunities not only enhance professional growth but also open doors to new collaborations and networks.
A Research paper must convince its readers to change their mindset about the research domain in question, to look at a problem differently, or to consider a new solution. Sometimes it is really challenging to convince your readers to read your paper and take up the work in your field and cite your paper in their research work.
How Citation Count of A Particular Research Paper will help a Journal?
The citation count of a particular paper can help a journal improve its ranking in a few ways:
- Impact Factor: The impact factor of a journal is calculated based on the average number of citations received by articles published in the journal in the preceding two years. Therefore, if a paper published in a journal receives a large number of citations, it can significantly increase the impact factor of the journal. As a result, the journal’s ranking may improve in comparison to other journals in its field.
- Cited Reference Search: Many databases, such as Web of Science and Scopus, allow users to conduct a “cited reference search” to find all papers that have cited a particular paper. If a paper published in a journal is frequently cited, it can increase the visibility of the journal and attract more citations to other papers published in the journal. This increased visibility can lead to an increase in submissions to the journal, which can further improve its ranking.
- Reputation: High citation counts can also help to establish the reputation of a journal within its field. Journals that are widely cited are often viewed as influential and important within their respective fields, which can attract submissions from high-quality researchers and lead to further citations.
Overall, the citation count of a particular paper can have a significant impact on the ranking of a journal. However, it is important to note that other factors, such as the quality of the papers published and the rigor of the peer-review process, also play a crucial role in determining a journal’s ranking.
I have written a comprehensive blog post on Unlocking the Mystery of Journal Rankings(Q1,Q2,Q3,Q4): A Comprehensive Guide. Please go through the post for in-depth knowledge of the journal ranking process.
How to Find the Citation Count of a Research Paper?
To find the citation count of a research paper, you can follow these steps:
- Start with academic search engines or databases: Some popular academic databases that provide citation information include Google Scholar, Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed. Access to these databases may vary depending on your institutional affiliation or subscription access.
- Search for the paper: Enter the title, author names, or keywords related to the paper you want to find citations for in the search bar of the chosen database.
- Locate the paper in the search results: Look for the paper you are interested in within the search results. It may help to verify that the paper’s title, authors, and publication details match your intended paper.
- View citation information: Once you have located the paper, you should be able to see its citation count or a link/button to view the citations. The exact location and presentation of citation information can vary between databases.
- Explore citation details: Clicking on the citation count or the “Cited by” link/button will typically lead you to a page displaying the papers that have cited the original paper. You can browse through this list to get a sense of who has referenced the paper and how it has influenced subsequent research.
It’s worth noting that different databases may provide slightly different citation counts, as they may have different coverage or methodologies for collecting citation data. It can be helpful to cross-reference multiple databases for a more comprehensive understanding of the citation count of a research paper.
How to Attract Citations for Your Research Paper?
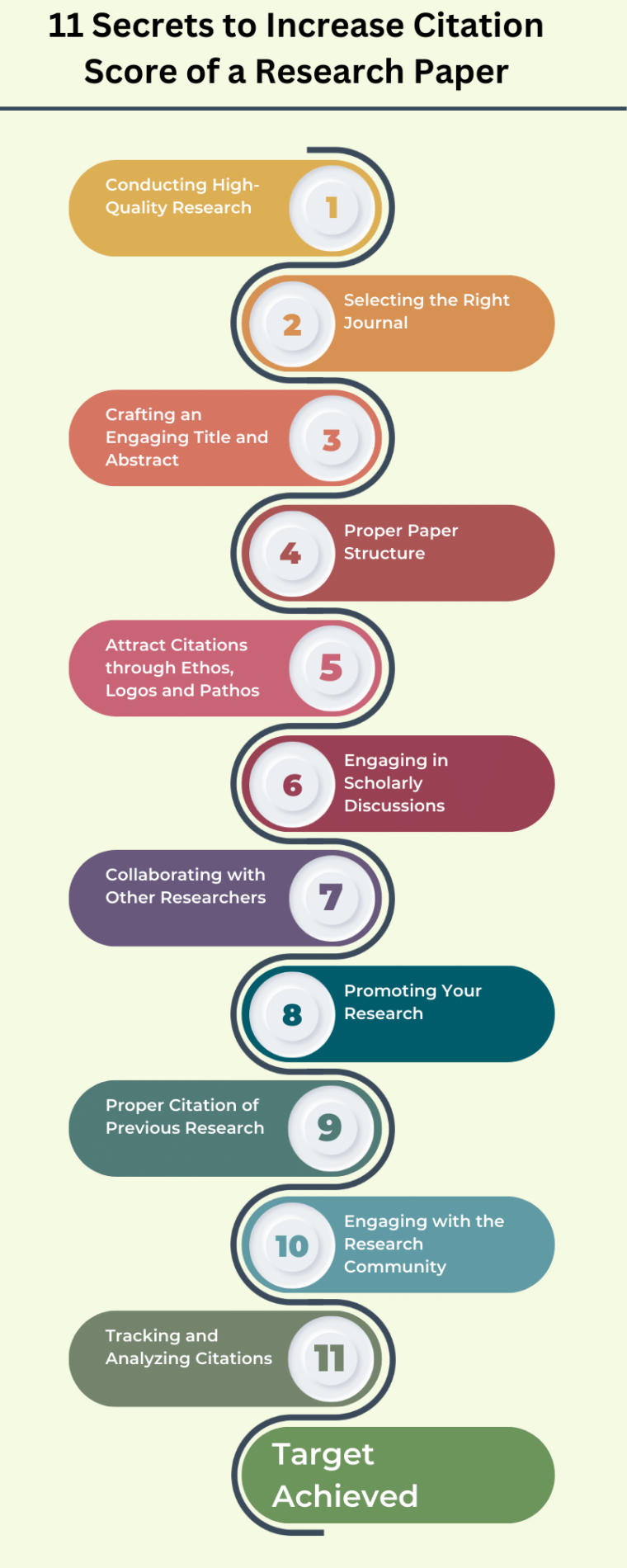
Listed below are the 11 strategies for enhancing your citation counts. By integrating these strategies into your research workflow, you can increase the citation counts of your research paper in a legitimate and ethical manner. Through these efforts, you will not only enhance the recognition and visibility of your work but also contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Remember, attracting citations and gaining recognition is a gradual process that requires perseverance, continuous learning, and active engagement with the research community. Your contributions to the scientific discourse will shape the future of your field and establish your position as a respected researcher.
1. Conducting High-Quality Research
Selecting a research topic that is significant and relevant to the field enhances the value and impact of your research. By addressing a pressing issue or exploring an emerging area, your research is more likely to attract attention and citations.
Example: Conducting a study on the impact of renewable energy policies on carbon emissions addresses the urgent need for sustainable solutions in combating climate change, making your research topic highly relevant and significant.
Employing a rigorous methodology and ensuring the reliability of your results strengthens the credibility of your research. Applying appropriate research design, data collection methods, and statistical analysis techniques enhances the validity and replicability of your findings.
Example: When conducting a clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of a new drug, ensuring a double-blind, randomized control design, meticulous data collection, and statistical significance testing helps establish the soundness of your methodology and the reliability of your results.
Identifying gaps or unanswered questions in existing research provides an opportunity to contribute new insights and knowledge to the field. Filling these gaps not only adds value to your research but also increases the chances of attracting citations from researchers interested in the same area.
Example: If previous studies on the impact of technology in education have focused on primary and secondary schools, conducting research that explores the effectiveness of educational technology in higher education addresses a gap in the literature and contributes to the understanding of technology’s role in different educational contexts.
2. Selecting the Right Journal
Aim to publish your research in journals that have a strong reputation and high impact factor within the computer science field. Publishing in such journals increases the visibility and reach of your research, attracting more citations from researchers in the community.
Example: For a computer vision research paper, targeting reputable journals like IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI) or ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) can significantly enhance the chances of receiving citations due to their high impact factor and wide readership.
Evaluate the scope and readership of potential journals to ensure your research aligns with the interests and focus of the journal’s audience. Publishing in journals that cater to the specific subfield or topic of your research increases the likelihood of attracting citations from researchers who are actively engaged in that area.
Example: If your research focuses on natural language processing and machine learning, considering journals like the Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR) or Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics (TACL) would be suitable choices as they have a dedicated readership interested in these topics.
Carefully read and adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the target journal. Structure your paper, format citations, and present your findings in a manner that aligns with the journal’s guidelines and standards.
Example: If you are submitting your research to a conference proceedings publication such as the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, ensure your paper follows the specified format, page limits, and citation style mandated by the conference proceedings.
By applying these principles within the computer science domain, you can increase the likelihood of selecting the right journal for your research, maximizing the visibility and citation potential of your work in the research community.
I have written an article on “How to select good quality journal paper for your research work”. Please visit the article for further details.
3. Crafting an Engaging Title and Abstract
A compelling title and informative abstract play a crucial role in grabbing the attention of readers and potential researchers. They serve as the first impression of your research and can significantly impact the number of readers and citations your work receives.
Example: Consider a research paper in the field of artificial intelligence and robotics. Instead of a generic title like “Robot Localization Techniques,” a more compelling title such as “Advanced Multi-Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Localization in Dynamic Environments” immediately captures the interest of readers and highlights the specific focus and novelty of the research.
Similarly, in the abstract, it is important to succinctly summarize the key aspects of your research, including the problem statement, methodology, and significant findings. For example, an informative abstract for a paper on computer vision could briefly highlight the use of deep learning algorithms to achieve state-of-the-art object recognition accuracy.
When crafting the title and abstract, it is essential to emphasize the significance and novelty of your research. This helps readers understand the unique contributions your work brings to the field and encourages them to delve deeper into your paper.
Example: Suppose you have developed a novel algorithm for real-time video object tracking. In the title and abstract, you could emphasize the real-time aspect and the improved accuracy of your algorithm compared to existing methods. This highlights the novelty of your approach and attracts researchers who are specifically interested in real-time tracking or seeking improvements in the field.
A well-crafted title and abstract should pique the curiosity of readers and encourage them to explore your research further. By providing a concise yet enticing summary of your work, you can engage readers and motivate them to read the full paper, potentially leading to more citations and recognition.
Example: Consider a paper on the application of machine learning techniques for sentiment analysis in social media. An abstract that highlights the potential impact of sentiment analysis on understanding public opinion, predicting trends, and making informed decisions in areas such as marketing or public policy can attract readers from various domains and encourage them to explore the full paper.
By carefully crafting an engaging title and abstract that effectively convey the significance, novelty, and potential impact of your research, you can capture the attention of readers, encourage further exploration, and increase the likelihood of receiving citations and recognition for your work.
Visit my articles on “Writing Abstract” and “Identifying Keywords for Research paper” for understanding the importance of abstract and keywords in helping to increase citation counts.
4. Proper Paper Structure
Organizing your paper in a logical and coherent manner is crucial for effectively presenting your ideas and findings. A well-structured paper helps readers navigate through your work smoothly and comprehend the flow of information.
Example: Let’s say you are writing a research paper on a new algorithm for image recognition. You would typically start with an introduction that provides background information, outlines the problem statement, and highlights the significance of the research. Then, you would proceed to the methodology section, where you explain the details of your algorithm and any associated techniques. The results section would present your experimental findings and evaluation metrics, followed by a discussion section where you interpret the results and discuss their implications. Finally, you would conclude the paper by summarizing the key findings and suggesting avenues for future research.
It is essential to clearly delineate sections for different components of your research paper, including the introduction, methodology, results, and discussion. Each section serves a specific purpose and should be clearly labelled and organized to ensure coherence and readability.
Example: In the introduction section, you would provide a concise overview of the problem you are addressing, the motivations behind your research, and the objectives of the study. The methodology section would then describe the algorithms, frameworks, or tools you employed to conduct your research and explain the steps involved. The results section would present the empirical outcomes, such as accuracy rates, performance metrics, or experimental data, while the discussion section would analyze and interpret those results, discussing their implications and potential limitations.
When writing a research paper, it is important to ensure that your paper is easily readable and comprehensible to both experts and non-experts in the field. This involves using clear language, concise explanations, and visual aids when necessary.
Example: To enhance readability, you can use subheadings within each section to divide the content into smaller, focused segments. Additionally, you can use figures, diagrams, or tables to illustrate complex concepts or present experimental results visually. This makes it easier for readers to grasp the main ideas and findings of your research.
By maintaining a proper paper structure, including logical organization, clear delineation of sections, and ensuring easy readability and comprehension, you can effectively present your research findings in the computer science domain. This enhances the overall quality of your paper, facilitates understanding for readers, and contributes to the credibility and impact of your research.
Refer my article on “How to Write a Research Paper in 11 easy steps” for further details on writing and structuring research paper.
5. Attract Citations through Ethos, Logos and Pathos
More than two thousand years back ancient Greek philosopher and scientist Aristotle suggested three simple techniques Ethos, Pathos and Logos (also called rhetorical appeals ) which writers and speakers must use to make their audience hook to their writing or speeches. These same techniques can be applied to research paper writing also. Let us look at these techniques and a few examples to show how you can convince your reader to read your paper.
A. Ethos

Ethos means “character” in Greek terminology and the word “ethics” is derived from “ethos”. As a paper writer, you should use ethos to show your audience that you have some credible information and you have carried out work with credible tools and technologies. You have to showcase your depth of understanding and knowledge by citing the following:
Cite the research papers of renowned authors (Domain Experts)
Those who have carried out work previously and whose works are published in reputed journals or patented.
Tools and Technologies
Use the tools and technologies which are used by the authors of reputed journals.
Data sets used
Select the data sets which are already used in some previous works or you have built them on your own under the supervision of some domain expert or Research Lab.
Example 1:
The following project is part of AICTE-funded Digital India project aimed at developing and integrating new ICT tools for improved government services.
Example 2:
The quality grading of Gauva fruit is developed to measure its effectiveness in developing medicines with the support of the faculty of the All India Medical Board.
Example 3:
Our project uses ABC Dataset [4] provided by the Indian Space Organization and XYZ image datasets[5] provided by the NASA website for all the experiments.
Example 4:
We have used the datasets of all human motions provided by RED Labs[8] for the country of Portugal.
Example 5:
The use of the MNR for training Neural Networks has been developed by Darren [9] one of the most popular researchers in Neural Networks.
Example 6:
In 1997, Alpen [2] senior scientist at CGHN Labs France, demonstrated the first successful application of the Back Propagation Neural Network method to the problem of user behaviour analysis.
B. Logos

” Logos” means “logic” in Greek terminology. As a writer, you should support the selection of your research topic and methodology of implementation by citing facts and statistics and other undeniable figures from reputed authorities in the concerned domain.
Example 1:
The following project is part of AICTE-funded Digital India project aimed at developing and integrating new ICT tools for improved government services.
Example 2:
The quality grading of Gauva fruit is developed to measure its effectiveness in developing medicines with the support of the faculty of the All India Medical Board.
Example 3:
As per the statistics given by the International Disability Council, around 15% of the world’s population has one or the other type of disability.
Example 4:
As per the estimates of the International Information Technology Association, the rapid growth in Platform as a Service (PaaS) in Cloud Computing is inevitable and it is estimated that nearly one-third of the worldwide enterprise application market will be PaaS-based by 2020, driving annual PaaS revenue to $800 million, from 300 million in 2012.”
Example 5:
The Indian cloud services market is projected to grow 30 per cent in 2015 to a total of $40 billion and up from $20 billion in 2014, according to ABC Market Research.
C. Pathos

In Greek terminology “suffering” and “experience” are referred to as Pathos. Sympathy, Empathy and Pathetic are derived from Pathos. A reader who goes through your paper and finds “Pathos”, will be more sympathetic towards the current issue at hand. Being a research paper writer, you need to identify a current burning issue that has necessitated the research you have undertaken and use pathos to make the audience feel sympathetic and anguish about the issue and continues research in the same field.
Example 1 :
Pathological issues in plants can increase the cost of agricultural production and can severely affect the economical condition of the producer if not detected in the early stage of disease development.
Example 2:
It is already an established fact that lung cancer is the major cause of death in men and women across the Globe.
Example 3:
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the major eye diseases which can harm diabetic patients severely. Many diabetic patients are affected by blindness and long-term vision defects due to DR.
6. Engaging in Scholarly Discussions
Actively participating in conferences, seminars, and workshops is a valuable way to engage in scholarly discussions in the domain of research. These events provide platforms for researchers to present their work, exchange ideas, and receive feedback from peers and experts in the field.
Example: Let’s say you have developed a new machine-learning algorithm for anomaly detection. By attending a machine learning conference, you can submit a paper or poster presentation about your algorithm. During the conference, you will have the opportunity to engage in discussions with other researchers who are interested in the same topic. You can present your findings, share insights, receive feedback on your work, and gain valuable perspectives from experts in the field.
When engaging in scholarly discussions, it is important to actively participate and interact with others. This can involve presenting your research at conferences or seminars, engaging in panel discussions, or participating in Q&A sessions. By sharing your work and engaging in discussions, you can receive feedback, exchange ideas, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the domain.
Example: Imagine you have conducted research on the use of blockchain technology in securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices. You can actively interact with others by presenting your research at a relevant conference or seminar. During your presentation, you can discuss the challenges you faced, the methodologies you employed, and the potential applications of your findings. By actively engaging with the audience and responding to their questions and comments, you can foster discussions and gain valuable insights from fellow researchers, industry professionals, and other attendees.
Engaging in scholarly discussions also provides an opportunity to network and foster collaborations with other researchers in the computer science domain. Building connections with like-minded individuals can lead to collaborations on future research projects, joint publications, and shared resources.
Example: Let’s say you are attending a workshop on artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. During the event, you can network with researchers, academics, and industry professionals who share your interest in AI applications in healthcare. By actively engaging in discussions and exchanging contact information, you can establish connections that may lead to collaborative research projects. For instance, you might meet researchers who have expertise in medical imaging and wish to collaborate on developing an AI-based diagnostic tool.
Engaging in scholarly discussions by participating in conferences, seminars, and workshops, presenting your research, actively interacting with others, and networking helps you stay updated on the latest advancements, receive feedback on your work, and establish meaningful collaborations in the domain. It fosters a vibrant research community and contributes to the overall growth and impact of your research.
7. Collaborating with Other Researchers
Collaboration with other researchers offers numerous benefits, including the opportunity to increase research citation counts. By actively seeking co-authorship and engaging in collaborative projects, you can leverage the expertise and knowledge of other researchers, expand the scope of your research, and enhance the quality and impact of your work.
Example: Let’s say you are working on a project related to developing a new algorithm for data compression. By collaborating with other researchers who specialize in different areas, such as signal processing or information theory, you can bring together diverse perspectives and complementary expertise. This collaboration can lead to a more comprehensive and robust research outcome. When the research paper resulting from this collaboration is published, it is likely to attract more attention, potentially increasing the number of citations.
Co-authored papers have the advantage of reaching a wider audience compared to individual-authored papers. Collaborating with other researchers can expose your work to new networks, communities, and readerships. This broader reach increases the visibility of your research and enhances the likelihood of receiving citations from researchers who may have otherwise not come across your work.
Example: Suppose you collaborate with researchers from different institutions or countries on a project related to natural language processing. By combining your efforts and publishing the research outcomes together, your paper can gain exposure to multiple research communities and attract citations from various sources. Researchers who specialize in linguistics, machine learning, or computational linguistics may find your work relevant and cite it in their own studies, thus increasing the citation count of your collaborative research.
Collaborating with other researchers increases the visibility of your research within the academic community. Through joint efforts, you can tap into each collaborator’s professional networks, promote your work collectively, and potentially increase the number of citations your research receives.
Example: Let’s say you form a collaboration with researchers who have strong connections in the computer vision research community. By working together and promoting your research through their networks, you can increase the visibility of your findings. This increased visibility can attract more attention, generate discussions, and result in a higher number of citations. Researchers who are actively engaged with your collaborators may discover your work, find it valuable, and cite it in their own publications.
By collaborating with other researchers, seeking co-authorship opportunities, leveraging the broader reach of co-authored papers, and enhancing visibility within the research community, you can increase the likelihood of receiving citations for your work. Collaboration not only expands the scope and impact of your research but also opens doors to new opportunities for recognition and growth in your academic career.
8. Promoting Your Research
In today’s digital age, academic social networking sites and personal websites play a crucial role in promoting your research. These platforms provide an avenue to showcase your work, establish your online presence, and connect with researchers in your field. By utilizing these platforms effectively, you can increase the visibility of your research and attract potential readers and collaborators.
Example: Suppose you are a computer science researcher working on the development of a novel machine-learning algorithm. Creating a profile on academic social networking sites like ResearchGate or Academia.edu allows you to share your research papers, project updates, and insights with a wide audience. You can also provide links to your personal website, where you can showcase your research accomplishments, publications, and relevant resources. By actively engaging with the community on these platforms, you can attract readers who are interested in your research area and potentially increase the citation count of your papers.
Sharing your research findings on relevant forums, blogs, and social media platforms can significantly contribute to increasing the visibility of your work. By participating in discussions, contributing to relevant blogs, and utilizing social media channels, you can reach a broader audience, including researchers, practitioners, and enthusiasts who may find your research valuable and cite it in their own work.
Example: Let’s say you have conducted research on the application of blockchain technology in cybersecurity. You can actively participate in online forums and discussion boards related to cybersecurity or blockchain technology and share insights from your research. Additionally, contributing guest posts to reputable blogs in your field can help you reach a wider audience and establish yourself as an expert in the domain. Furthermore, leveraging social media platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, or Reddit, where discussions and information sharing are prevalent, can lead to increased visibility, engagement, and potential citations.
The primary goal of promoting your research is to increase its visibility and attract readers and collaborators. By employing various promotion strategies, you can raise awareness about your work, spark interest among researchers and practitioners, and foster collaborations that can contribute to increased citation counts and recognition.
Example: Suppose you have developed a new algorithm for optimizing cloud resource allocation. By actively promoting your research through academic networks, social media, and conferences, you can capture the attention of researchers, industry professionals, and fellow academics who are working in the field of cloud computing. This increased visibility may lead to collaborations with experts in the domain, joint research projects, and co-authorship opportunities, all of which can enhance the impact and citation potential of your work.
By utilizing academic social networking sites and personal websites, sharing findings on relevant forums, blogs, and social media, and actively promoting your research to increase visibility and attract readers and collaborators, you can effectively raise awareness about your work and increase the likelihood of receiving citations. These promotion strategies help you connect with a broader audience, foster collaborations, and establish your presence in the research community.
9. Proper Citation of Previous Research
Properly citing previous research demonstrates your knowledge of the existing literature in your field. By acknowledging the work of other researchers, you show that you have conducted a comprehensive literature review and understand the context in which your research is situated. This not only enhances the credibility of your work but also helps to establish your expertise in the field.
Example: Let’s say you are conducting research on the effects of climate change on biodiversity. In your introduction section, you can cite previous studies that have examined similar relationships between climate change and biodiversity loss. By referencing these studies, you showcase your familiarity with the existing literature and demonstrate that your research builds upon previous knowledge in the field.
Properly citing relevant and influential works allows you to acknowledge the contributions of other researchers and integrate their findings into your own research. This not only strengthens the credibility of your work but also demonstrates your ability to situate your research within the broader scholarly conversation. Additionally, citing influential works can help to draw attention to your research and increase its visibility among researchers in your field.
Example: Suppose you are writing a research paper on deep learning algorithms for image recognition. In your methodology section, you can cite seminal papers or influential research studies that have introduced or advanced the state-of-the-art deep learning techniques you are utilizing. By citing these works, you acknowledge their impact on the field and position your research within the established body of knowledge.
Proper citation of previous research helps to build connections with other researchers and increases the likelihood of receiving reciprocal citations. When you appropriately cite and acknowledge the work of others, you establish a professional relationship with those researchers and contribute to the scholarly dialogue. This can lead to future collaborations, invitations to contribute to joint projects, and an increased chance of your work being cited by others in return.
Example: Imagine you have published a research paper on the applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare. In your discussion section, you cite the work of other researchers in the field who have made significant contributions to the same topic. By doing so, you not only recognize their work but also open avenues for potential collaborations or invitations to participate in future research projects related to AI in healthcare. Moreover, when you contribute valuable insights and cite other researchers’ works, they may be more likely to reciprocate by citing your work in their future publications.
By demonstrating knowledge of the existing literature, appropriately citing relevant and influential works, and building connections with other researchers through proper citation, you establish yourself as a well-informed and credible contributor to the research community. These practices not only enhance the quality and impact of your own research but also increase the chances of receiving citations from other researchers in return, thereby further boosting the recognition and visibility of your work.
10 Engaging with the Research Community
Actively participating in discussions and providing feedback on research papers, conferences, online forums, or social media platforms is a valuable way to engage with the research community. By sharing your insights, opinions, and constructive feedback, you contribute to the ongoing conversation in your field. Active participation demonstrates your knowledge and expertise, helps you stay updated with the latest advancements, and allows you to connect with other researchers who share similar interests.
Example: Let’s say you are attending a conference in the field of machine learning. During a panel discussion, you actively engage by asking thoughtful questions to the panelists and sharing your own insights on the topic. Your active participation not only showcases your expertise but also encourages meaningful discussions among fellow researchers. Additionally, your valuable feedback on other researchers’ presentations or papers can contribute to the improvement of their work and foster a collaborative environment.
Commenting on other researchers’ work and sharing your insights is another way to engage with the research community. By providing constructive comments or adding valuable perspectives to existing research, you contribute to the knowledge exchange and stimulate further discussions. This helps you establish your presence within the community and build connections with other researchers who are working on similar topics.
Example: Suppose you come across a published research article in your field that aligns with your own area of interest. You read the article thoroughly and leave a comment highlighting the strengths of the research, suggesting potential extensions, or asking clarifying questions. Your comment not only acknowledges the efforts of the authors but also showcases your understanding of the subject matter. Engaging in such discussions can lead to fruitful exchanges with the authors and other readers, fostering collaboration and expanding your network within the research community.
Engaging with the research community helps establish your presence and credibility as a researcher. By actively participating, providing feedback, and sharing insights, you showcase your expertise, build a reputation within your field, and create opportunities for collaboration. Establishing a strong presence and fostering collaboration can lead to joint research projects, invitations to contribute to publications or conferences, and increased recognition and visibility for your own work.
Example: Imagine you regularly participate in online forums or social media groups dedicated to artificial intelligence research. By consistently contributing valuable insights, sharing relevant resources, and actively engaging with other members, you establish yourself as an active and knowledgeable participant in the research community. This can lead to collaborations with researchers who have similar research interests, invitations to co-author papers or chapters in books, or even speaking opportunities at conferences or workshops. Establishing your presence and fostering collaboration opens doors to new opportunities and enhances your visibility and recognition within the research community.
Engaging with the research community through active participation, providing feedback, commenting on others’ work, and establishing your presence fosters a collaborative and intellectually stimulating environment. It allows you to contribute to the ongoing research discourse, expand your professional network, and increase the visibility and recognition of your own work within the community.
11. Tracking and Analyzing Citations
To track and analyze citations of your research paper, you can utilize various platforms such as Google Scholar, Scopus, or Web of Science. These platforms provide comprehensive databases of scholarly articles and citations, allowing you to search for your own publications and monitor how they are being cited by other researchers. By using these platforms, you can gather information on the number of citations, who has cited your work, and where it has been cited.
Example: Let’s say you published a research paper on a novel algorithm for image recognition in a computer science journal. By using Google Scholar, you can search for your paper and retrieve information about its citations. You find that several researchers have cited your work in their own studies, indicating its impact and influence in the field. This enables you to track the reach of your research and identify potential collaborations or areas of interest for further exploration.
Tracking citation counts is essential to gauge the impact and recognition of your research. By monitoring how often your work is cited, you can assess its influence within the scientific community and identify trends or patterns in its citation trajectory. Analyzing citation counts also helps you understand the broader impact of your research and its relevance to other studies in your field.
Example: Suppose you discover that your research paper on cybersecurity techniques has received a significant number of citations over time. This indicates that your work has resonated with other researchers and has been considered valuable and influential. By comparing citation counts with other papers in your field, you can evaluate the impact of your research and determine its significance within the broader research landscape.
Tracking and analyzing citations not only provide insights into the impact of your research but also help identify opportunities for further promotion or extension of your work. By examining the context in which your research is cited, you can identify potential collaborations, areas of interest for future studies, or gaps in the existing literature that your work can address. This knowledge allows you to strategically plan your research trajectory and maximize the visibility and impact of your work.
Example: Suppose you notice that researchers frequently cite your work when discussing the challenges of data privacy in the era of big data. This indicates that your research has contributed valuable insights into this specific area. Recognizing this trend, you can focus on further exploring and publishing-related studies to establish yourself as an authority in the field. Additionally, you can proactively engage with researchers who have cited your work to foster collaborations and explore opportunities for joint projects.
By actively tracking and analyzing citations, you gain valuable information about the impact of your research, identify potential collaborations, and uncover new areas for exploration and promotion. It helps you stay informed about the influence of your work and strategically plan your research trajectory to increase its visibility and recognition within the research community.
Conclusion
Increasing citation counts and gaining recognition for your research paper requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses various strategies and actions. By implementing the principles discussed above, you can enhance the visibility, impact, and credibility of your work in the research community.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many citations is good for a research paper?
The number of citations considered “good” for a research paper can vary depending on several factors, such as the field of study, the publication venue, and the specific context. There isn’t a universally defined threshold for what is considered a good number of citations. However, higher citation counts generally indicate that a paper has had a significant impact and influence within its research community.
In some fields, such as highly specialized or niche areas, a paper with a few dozen citations might be considered significant. In contrast, in more established or widely studied fields, a good paper could have hundreds or even thousands of citations. It’s important to note that citation counts can also be influenced by factors like the quality and significance of the research, the reputation of the authors, and the visibility of the publication venue.
Is it possible that my citation count get reduce?
It is possible for your citation count to be reduced over time. There are a few reasons why this might happen:
Retractions or corrections: If a paper is found to have significant errors, misconduct, or ethical issues, it may be retracted or corrected by the authors or the journal. In such cases, citations to the paper may be removed or discounted, which can lead to a reduction in the citation count.
Removal of duplicates or self-citations: Sometimes, databases or indexing systems may identify duplicate or self-citations and remove them from the citation count. This can occur if the same paper is cited multiple times within the same publication or if an author excessively cites their own work to artificially inflate their citation count.
Changes in database coverage or indexing: Citation counts can also fluctuate if there are changes in the databases or indexing systems used to calculate the counts. For example, if a paper was previously indexed by a particular database but is later excluded or not properly indexed, its citation count may decrease.
Citation errors or omissions: Mistakes can occur when citing papers, such as misspelling author names, incorrectly listing publication details, or omitting citations altogether. If these errors are discovered and corrected, it could lead to a decrease in the citation count of the affected paper.
What are indirect citations?
Indirect citation refers to the act of citing a source that was cited in another source, rather than directly citing the original source itself. It occurs when a researcher wants to reference a particular idea, information, or finding from a source but discovers it through another work that has already referenced it.
Here’s an example to illustrate indirect citation:
Let’s say you are reading a research article by Author A, and within that article, Author A mentions a study conducted by Author B that is relevant to your research. Instead of going back to the original study by Author B and citing it directly, you decide to cite Author A’s article, which indirectly refers to the study by Author B.
Indirect citations are commonly used in research when the original source is not directly accessible, when the original source is in a language that the researcher does not understand, or when the researcher wants to acknowledge the contribution of the author who cited the original work.
Can I cite my own paper (Self citation)?
It is acceptable and common to cite your own previous work, which is known as self-citation. Self-citation is a way to acknowledge your previous research that is directly relevant to your current work. It allows you to build upon your earlier findings, provide additional context, or reference methodologies or data that you have previously published.
It’s important to note that self-citation should not be used solely for the purpose of inflating your citation count or manipulating impact metrics. Responsible self-citation should be based on the merits of the research and its contribution to the current work.
Citation count web of science vs google scholar
Web of Science and Google Scholar are two popular platforms that provide citation counts, but they have different coverage and methodologies, which can lead to variations in the citation counts they display.
Web of Science: Web of Science is a subscription-based citation database that focuses on academic journals and conference proceedings. It has a more selective and curated approach to indexing and includes a wide range of disciplines. Web of Science provides citation counts based on the number of times a paper has been cited within the journals and conference proceedings it covers. It offers features like the h-index, which is a measure of both the productivity and impact of an author’s work.
Google Scholar: Google Scholar, on the other hand, is a free search engine that indexes a broader range of sources, including academic papers, theses, preprints, books, conference proceedings, and more. It has a wider coverage, but its indexing is automated and can include sources that may not undergo the same rigorous peer-review process as those indexed by Web of Science. Google Scholar counts citations from various sources, including both peer-reviewed and non-peer-reviewed publications, as well as citations from websites, institutional repositories, and other non-traditional sources.